本文解释了物理学中的位置向量是什么。因此,您将逐步了解位置向量的属性是什么、如何计算点的位置向量以及具体示例。
什么是位置向量?
位置向量,或简称为位置向量,是描述点相对于参考系的位置的向量。即位置向量用于表示坐标系中点的位置。
从数学上讲,点的位置向量定义为从坐标原点到该点的向量。因此,通过将该点的坐标减去原点坐标来计算该点的位置向量。
![]()
一般来说,位置向量用单位向量表示
![]()
,
![]()
和
![\vv{k}[/latex ] , qui correspondent respectivement aux coordonnées des axes X, Y et Z. Par exemple, si les coordonnées cartésiennes d'un point sont (3,4,5), le vecteur position de ce point est r=3i+4j+5k.
<figure class="wp-block-image aligncenter size-full is-resized"><img decoding="async" loading="lazy" src="https://physigeek.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/vecteur-de-position.png" alt="vecteur de position" class="wp-image-7644" width="374" height="308" srcset="https://physigeek.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/vecteur-de-position-300x247.png 300w, https://physigeek.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/vecteur-de-position.png 697w" sizes="(max-width: 300px) 100vw, 300px"></figure>
<h2 class="wp-block-heading"><span class="ez-toc-section" id="Caracteristicas-del-vector-de-posicion"></span> Caractéristiques du vecteur de position<span class="ez-toc-section-end"></span></h2>
<p> Maintenant que nous connaissons la définition du vecteur position, voyons quelles sont ses caractéristiques.</p>
<ul style="color:#4fd12f; font-weight: bold;">
<li style="margin-bottom:20px"> <span style="color:#101010;font-weight: normal;">Le vecteur position d’un point est défini comme la différence entre les coordonnées de ce point et l’origine des coordonnées. Par conséquent, la formule pour calculer le vecteur position d’un point est la suivante :</span></li>
<p> [latex]\vv{r}=PO” title=”Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com” height=”438″ width=”1546″ style=”vertical-align: -5px;”></p>
</p>
<li style=](https://physigeek.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-493ea824d13cdf2c289249ee201f0079_l3.png) 点的位置向量的坐标用单位向量表示
点的位置向量的坐标用单位向量表示
![]()
,
![]()
和
![\vv{k}[ /latex], qui représentent respectivement les directions des axes OX, OY et OZ.</span></li>
<p> [latex]\vv{r}=x\vv{i}+y\vv{j}+z\vv{k}” title=”Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com” height=”41″ width=”616″ style=”vertical-align: -5px;”></p>
<p><span style=](https://physigeek.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-9a41deb220b0257eea947e8a946f9a2f_l3.png) 位置矢量的方向是将标记原点与所考虑的点连接起来的线。
位置矢量的方向是将标记原点与所考虑的点连接起来的线。
![]()
请注意,如果我们在平面上工作,位置向量将只有两个坐标 (x,y)。另一方面,如果我们在空间中工作,位置向量将具有三个坐标(x,y,z)。
位置向量练习已解决
为了更好地理解这个概念,下面是一个关于如何计算位置向量的已解决练习。
- 物体的位置与时间向量由以下表达式定义。计算 t=3 s 时刻物体的位置向量及其模。
![]()
要找到时间 t=3 s 时的位置向量,您必须将参数 t 替换为其值并进行计算:
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \begin{aligned}\vv{r}(3)&=4\cdot 3\vv{i}+2\cdot 3^2\vv{j}+5 \vv{k}\\[2ex ]\vv{r}(3)&=12\vv{i}+18\vv{j}+5\vv{k}\end{aligned}](https://physigeek.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-dec24ff071b35d8e731e7a0a66d6c0e0_l3.png)
然后我们通过计算坐标平方和的平方根来输出位置向量的模:
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \begin{aligned}|\vv{r}(3)|&=\sqrt{12^2+18^2+5^2}\\[2ex]|\vv{r}(3)| &=\sqrt{493}\end{aligné}](https://physigeek.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-8c09dc9fc6db4d03b23adfc1b44c8168_l3.png)
位置和位移矢量
点的偏移定义为终点与起点之间的距离。因此,位移矢量就是最终位置矢量减去初始位置矢量得到的矢量。
![]()
因此,位置矢量和位移之间的区别在于,位置矢量表示物体在给定时间的位置,而位移矢量表示运动物体的两个不同位置之间的距离。
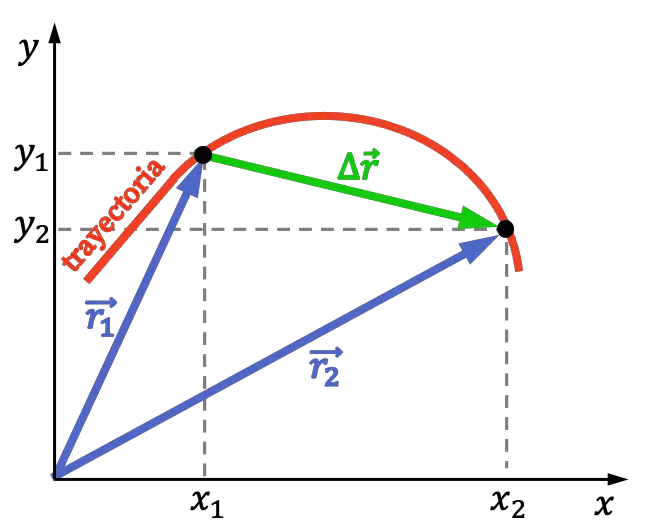
同样,路线的移动也必须有所区别。路径是指走过的路径的总长度,而位移是指从最终位置到最终位置的距离。因此,路径可以大于偏移量。